Test Bank for Statistics for Nursing Research A Workbook for Evidence-Based Practice 3rd Edition by Susan K. Grove All Chapters 2025
Course:
Nursing
Institution:
Nursing
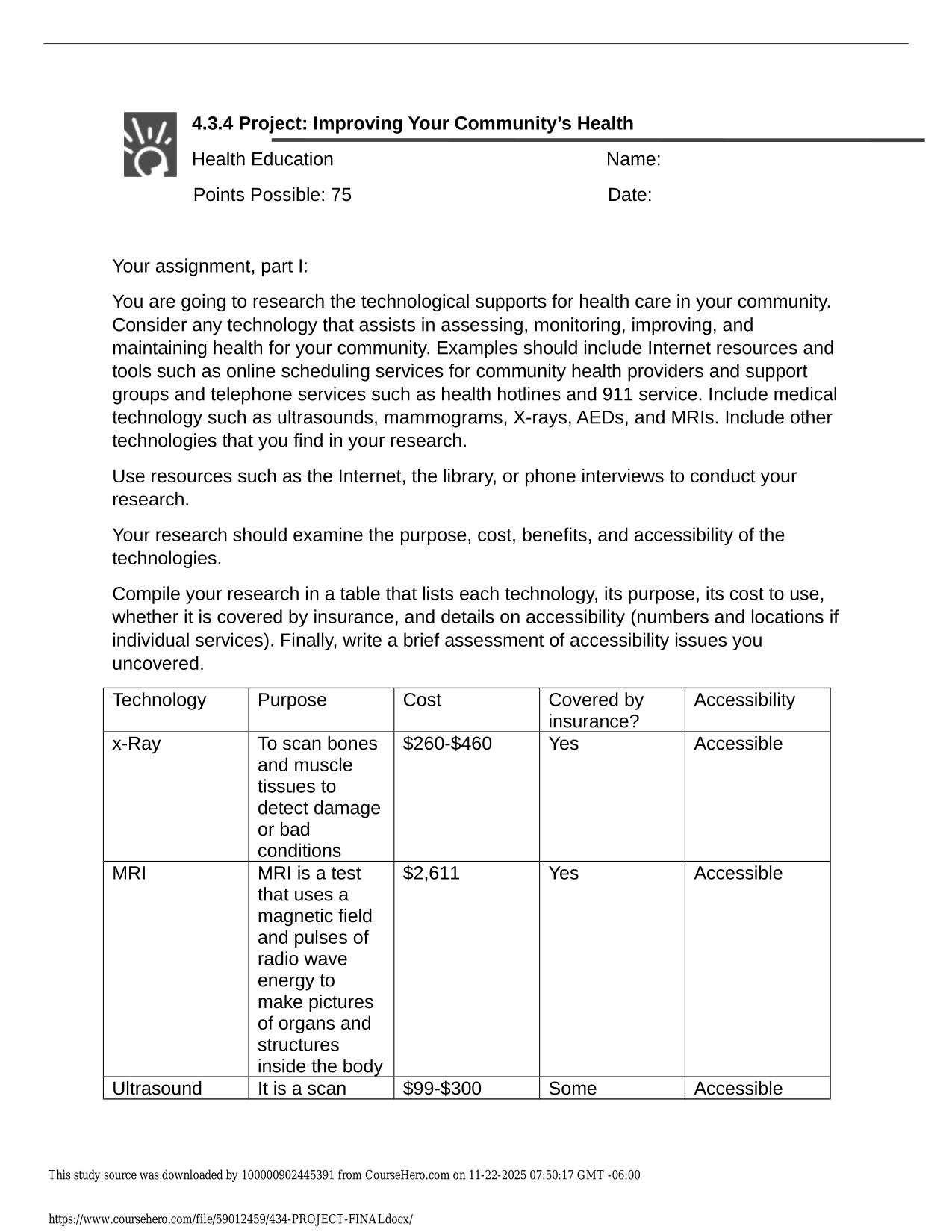
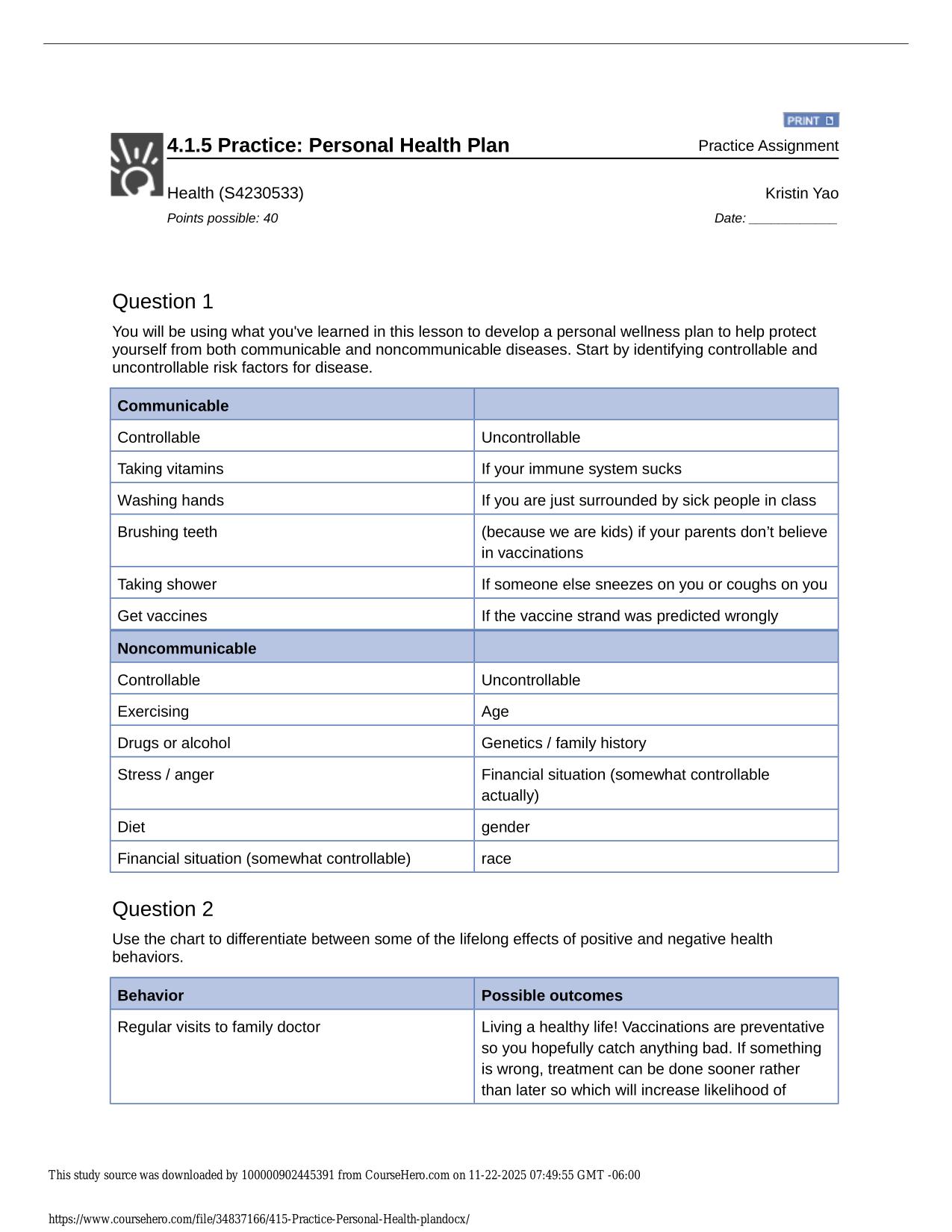
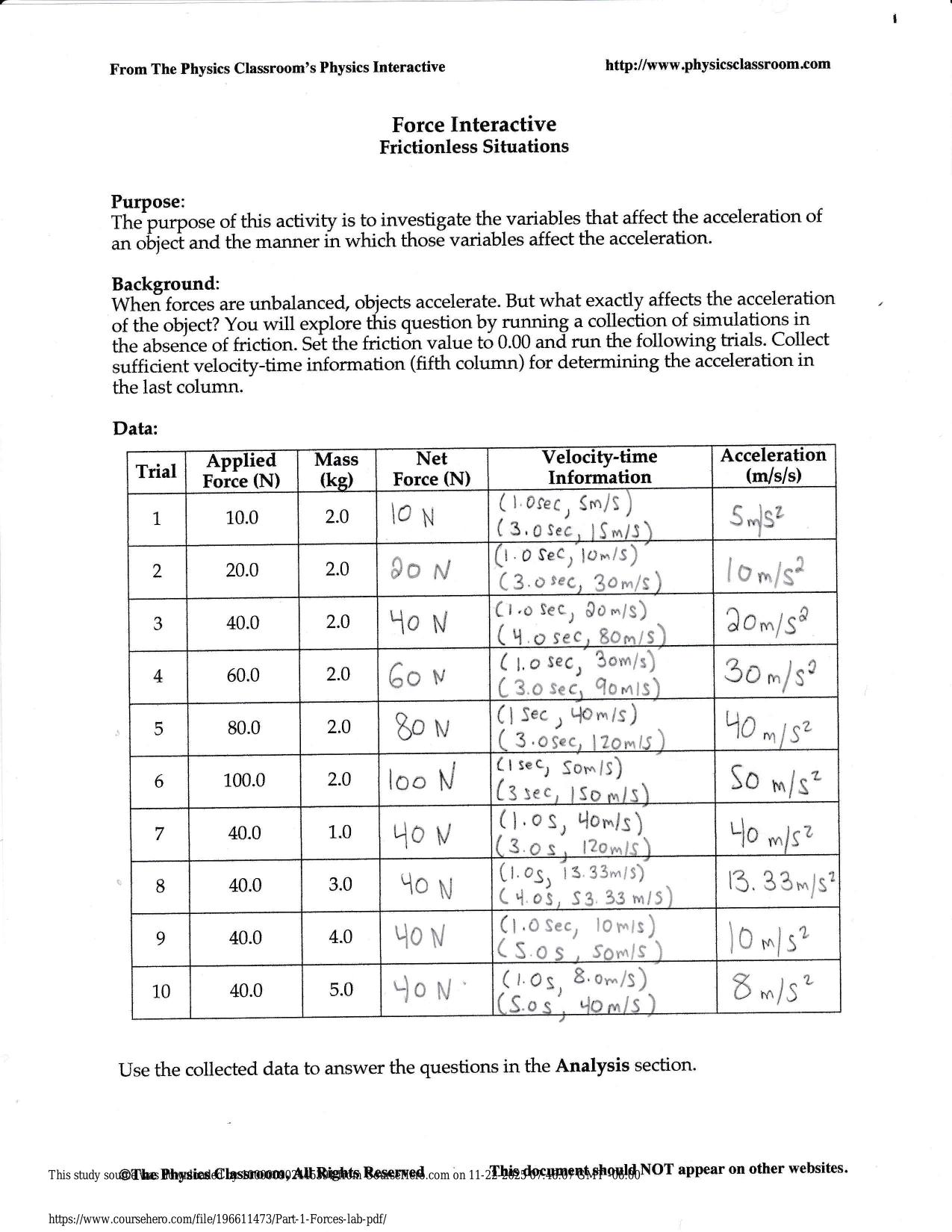
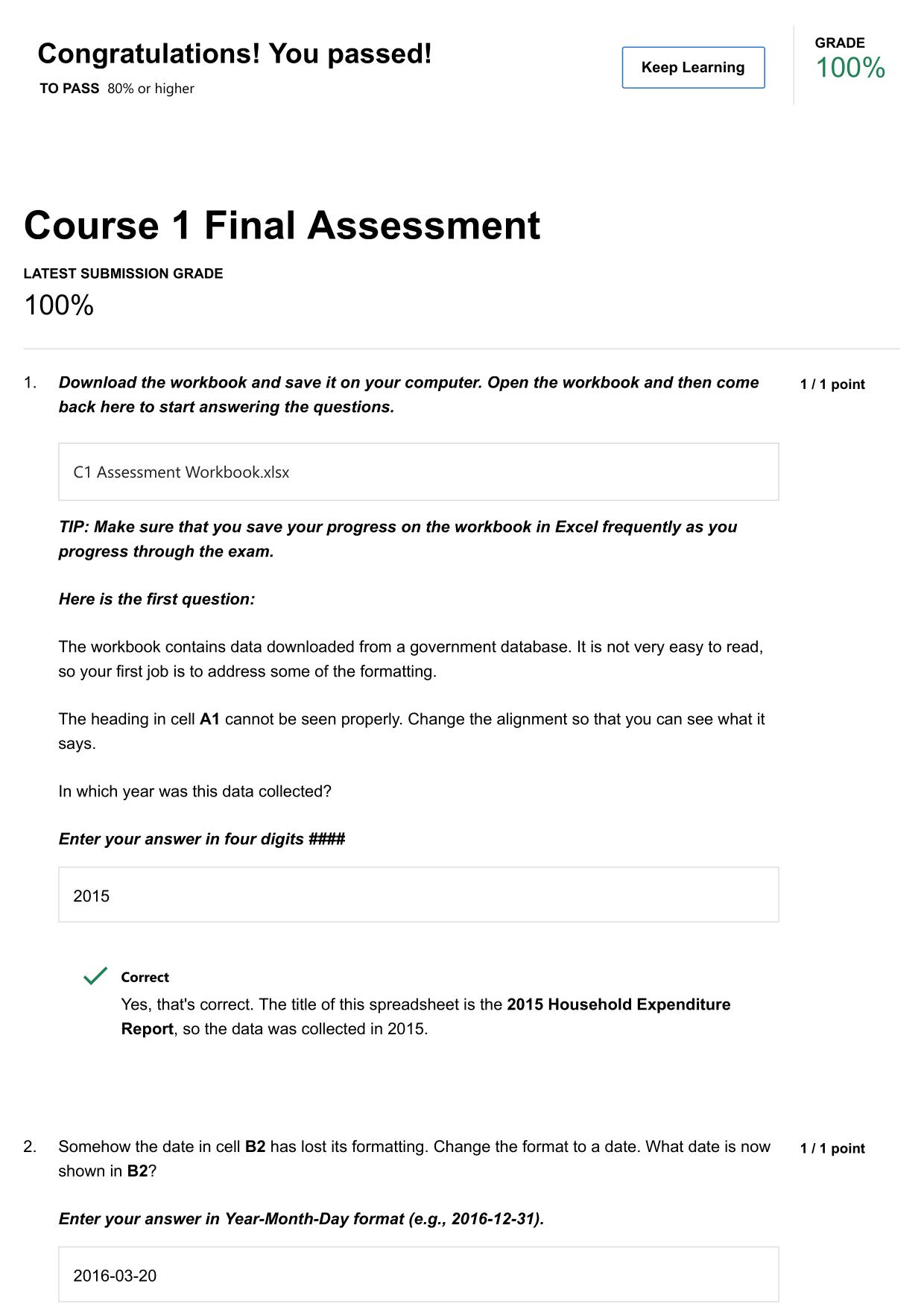
Test Bank for Statistics for Nursing Research A Workbook for Evidence-Based Practice 3rd Edition by Susan K. Grove All Chapters 2025 The questions are in bold followed by answers. 1. In Table 1 , identify the level of measurement for the current ther...
After purchase, you get:
✅ Instant PDF Download
✅ Verified answer explanations
✅ Refund if not Satisfied
✅ Prepared for 2025/2026 test cycle
Overview
The format encourages learners to think critically about each step, promoting deeper conceptual comprehension. You're developing the habit of questioning your own reasoning and verifying your thought process. This metacognitive approach leads to more robust understanding and better problem-solving skills. Students often carry this critical thinking habit into their other academic work and professional lives. Test Bank for Statistics for Nursing Research A Workbook for Evidence-Based Practice 3rd Edition by Susan K. Grove All Chapters 2025 equips learners with the fundamental tools needed to navigate challenging Nursing exam material. From time management strategies to content mastery techniques, you'll develop a complete skill set for exam success. These tools become part of your permanent learning toolkit, valuable for future educational challenges as well. Many students find they become better learners overall after working with these materials.
Who Is This For?
specific toward test-takers who want curated, mistake-free, and carefully formatted revision material for Bank for Statistics for Nursing Research A Workbook for Evidence-Based Practice 3rd Edition by Susan K. Grove All Chapters. Users appreciate the attention to detail and accuracy. The clean presentation makes studying more productive and less frustrating. Perfect for busy learners seeking an streamlined, exam-focused preparation tool in Nursing. Many working professionals find it fits well into their hectic schedules. The focused content helps maximize study sessions, even when time is limited.
Related Keywords
Detailed Study Description
Frequently Asked Questions
Document Information
| Uploaded on: | November 1, 2025 |
| Last updated: | November 17, 2025 |
| Number of pages: | 76 |
| Written in: | 2025/2026 |
| Type: | Exam (elaborations) |
| Contains: | Questions & Answers |
| Tags: | Test Bank for Statistics for Nursing Research A Workbook for Evidence-Based Practice 3rd Edition by Susan K. Grove All Chapters 2025 The questions are in bold followed by answers. 1. In Table 1 , identify the level of measurement for the current therapy variable. Provide a rationale for your answer. Answer: The current therapy variable was measured at the nominal level. These drug categories were probably developed to be exhaustive for this study and included the categories of drugs the subjects were receiving. However, the categories are not exclusive, since patients are usually on more than one category of these drugs to manage their health problems. The current therapies are not measured at the ordinal level because they cannot be rank ordered, since no drug category can be considered more or less benefi cial than another drug category (see Figure 1-1 ; Grove & Gray, 2019 ). 2. What is the mode for the current therapy variable in this study? Provide a rationale for your answer. Answer: The mode for current therapy was b blocker. A total of 100 (94%) of the cardiac patients were receiving this category of drug, which was the most common prescribed drug for this sample. 3. What statistics were conducted to describe the BMI of the cardiac patients in this sample? Discuss whether these analysis techniques were appropriate or inappropriate. Answer: BMI was described with a mean and standard deviation (SD). BMI measurement resulted in ratio-level data with continuous values and an absolute zero ( Stone & Frazier, 2017 ). Ratiolevel data should be analyzed with parametric statistics such as the mean and SD ( Grove & Gray, 2017 ; Knapp, 2017 ). 4. Researchers used the following item to measure registered nurses’ (RNs) income in a study: What category identifies your cur |
Seller Information

AdelineJean
User Reviews (0)
Exam (Elaborations)
$13.00
Add to Cart
100% satisfaction guarantee
Refund Upon dissatisfaction
Immediately available after purchase
Available in Both online and PDF
$13.00
| 0 sold
Discover More resources
Inside The Document
Solution Manual for Statistics for Nursing Research A Workbook for Evidence-Based Practice 3rd Edition Susan Grove Daisha Answer Guidelines for Questions to Be Graded Identifying Levels of Measurement: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, and Ratio EX ERCIS E 1 The questions are in bold followed by answers. 1. In Table 1, identify the level of measurement for the current therapy variable. Provide a rationale for your answer. Answer: The current therapy variable was measured at the nominal level. These drug categories were probably developed to be exhaustive for this study and included the categories of drugs the subjects were receiving. However, the categories are not exclusive, since patients are usually on more than one category of these drugs to manage their health problems. The current therapies are not measured at the ordinal level because they cannot be rank ordered, since no drug category can be considered more or less beneficial than another drug category (see Figure 1-1; Grove & Gray, 2019). 2. What is the mode for the current therapy variable in this study? Provide a rationale for your answer. Answer: The mode for current therapy was  blocker. A total of 100 (94%) of the cardiac patients were receiving this category of drug, which was the most common prescribed drug for this sample. 3. What statistics were conducted to describe the BMI of the cardiac patients in this sample? Discuss whether these analysis techniques were appropriate or inappropriate. Answer: BMI was described with a mean and standard deviation (SD). BMI measurement resulted in ratio-level data with continuous values and an absolute zero (Stone & Frazier, 2017). Ratiolevel data should be analyzed with parametric statistics such as the mean and SD (Grove & Gray, 2017; Knapp, 2017). 4. Researchers used the following item to measure registered nurses’ (RNs) income in a study: What category identifies your current income as an RN? a. Less than $50,000 b. $50,000 to 59,999 c. $60,000 to 69,999 d. $70,000 to 80,000 e. $80,000 or greater What level of measurement is this income variable? Does the income variable follow the rules outlined in Figure 1-1? Provide a rationale for your answer. Answer: In this example, the income variable is measured at the ordinal level. The income categories are exhaustive, ranging from less than $50,000 to greater than $80,000. The two open-ended AG 1-1 AG 1-2 Answer Guidelines for Questions to Be Graded categories ensure that all salary levels are covered. The categories are not exclusive, since categories (d) and (e) include an $80,000 salary, so study participants making $80,000 might mark either (d) or (e) or both categories, resulting in erroneous data. Category (e) could be changed to greater than $80,000, making the categories exclusive. The categories can be rank ordered from the lowest salary to the highest salary, which is consistent with ordinal data (Grove & Gray, 2019; Waltz et al., 2017). 5. What level of measurement is the CDS score? Provide a rationale for your answer. Answer: The CDS score is at the interval level of measurement. The CDS is a 26-item Likert scale developed to measure depression in cardiac patients. Study participants rated their symptoms on a scale of 1 to 7, with higher numbers indicating increased severity in the depression symptoms. The total scores for each subject obtained from this multi-item scale are considered to be at the interval level of measurement (Gray et al., 2017; Waltz et al., 2017). 6. Were nonparametric or parametric analysis techniques used to analyze the CDS scores for the cardiac patients in this study? Provide a rationale for your answer. Answer: Parametric statistics, such as mean and SD, were conducted to describe CDS scores for study participants (see Table 1). CDS scores are interval-level data as indicated in Questions 5, so parametric statistics are appropriate for this level of data (Gray et al., 2017; Kim & Mallory, 2017). 7. Is the prevalence of depression linked to the NYHA class? Discuss the clinical importance of this result. Answer: The study narrative indicated that the prevalence of depression increased with the greater NYHA class. In NYHA class III, 64% of the subjects were depressed, whereas 11% of the subjects were depressed in NYHA class I. Thus, as the NYHA class increased, the number of subjects with depression increased. This is an expected finding because as the NYHA class increases, cardiac patients have more severe physical symptoms, which usually result in emotional distress, such as depression. Nurses need to actively assess cardiac patients for depression, especially those in higher NYHA classes, so they might be diagnosed and treated as needed. 8. What frequency and percent of cardiac patients in this study were not being treated with an antidepressant? Show your calculations and round your answer to the nearest whole percent (%). Answer: A total of 106 cardiac patients participated in this study. The sample included 15 patients who were receiving an antidepressant (see Table 1). The number of cardiac patients not treated for depression was 91 (106 – 15 ⫽ 91). The group percent is calculated by the following formula: (group frequency ⫼ total sample size) ⫻ 100%. For this study, (91 patients ⫼ 106 sample size) ⫻ 100% ⫽ 0.858 ⫻ 100% ⫽ 85.8% ⫽ 86%. The final answer is rounded to the nearest whole percent as directed in the question. You could have also subtracted the 14% of patients treated with antidepressants from 100% and obtained the 86% who were not treated with an antidepressant. 9. What was the purpose of the 6-minute walk test (6MWT)? Would the 6MWT be useful in clinical practice? Answer: Ha et al. (2018) stated, “The 6-min walk test (6MWT) is a measure of the submaximal, steady-state functional capacity” of cardiac patients. This test would be a quick, easy way to determine a cardiac patient’s functional status in a clinical setting. This functional status score could be used to determine the treatment plan to promote or maintain functional status of cardiac patients. Answer Guidelines for Questions to Be Graded AG 1-3 10. How was exercise confidence measured in this study? What was the level of measurement for the exercise confidence variable in this study? Provide a rationale for your answer. Answer: Exercise confidence of the patients with heart failure (HF) in this study was measured with the Exercise Confidence Scale that included four subscales focused on walking, climbing, lifting objects of graded weight, and running (see the study narrative). This was a rating scale with values ranging from 0 to 100. The patients’ scores for the Total Exercise Confidence scale and the subscales were considered interval-level data and analyzed with parametric statistics, such as means and SDs (see the study narrative; Waltz et al., 2017). Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
CourseHero & Studypool Unlocks
Get Unlocked CourseHero and Studypool documents files instantly to your email, simply by pasting your link and clicking "Unlock Now". Learn more on how to unlock here.