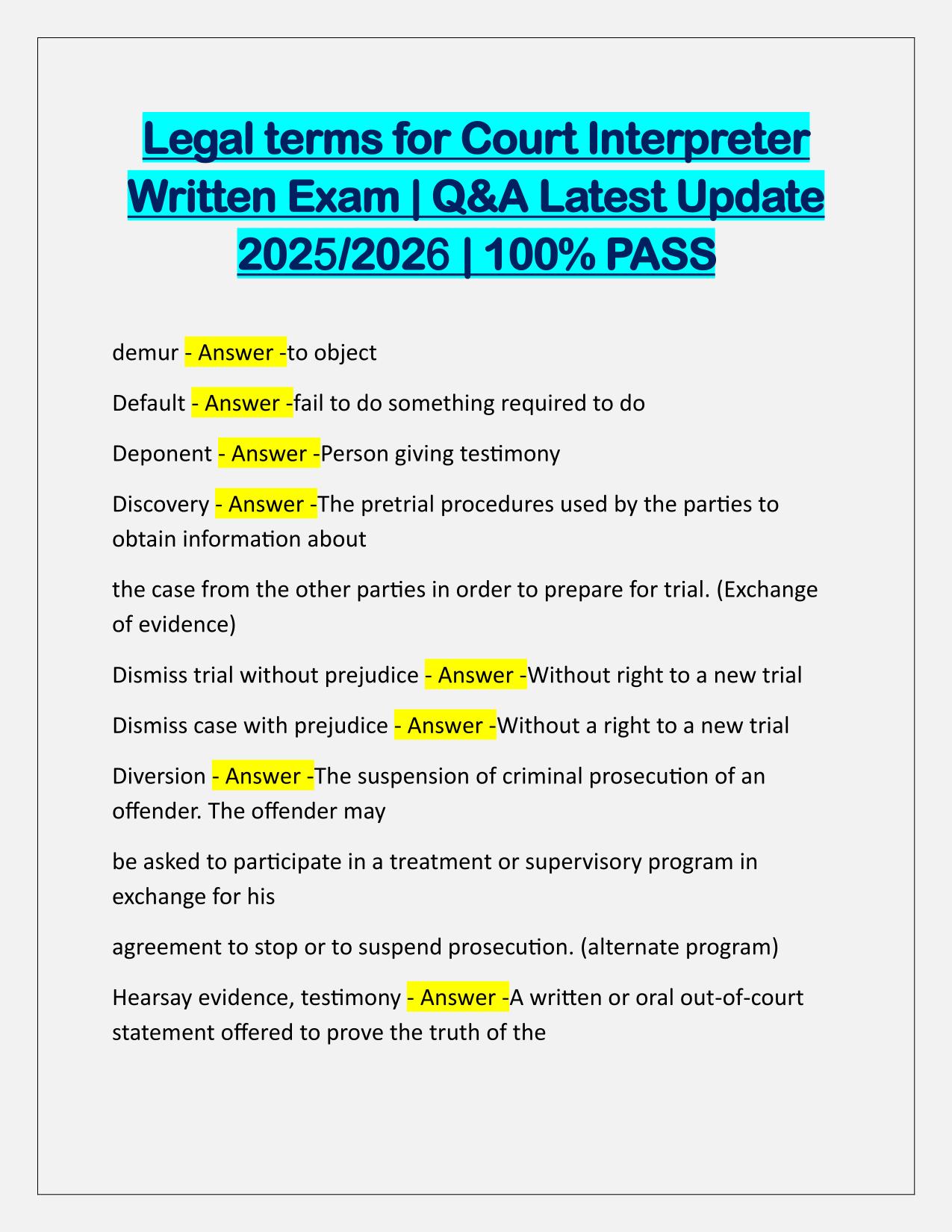
What to Expect in the NR 503 Midterm and Final EXAMS 2025/2026 (with PDF Questions & Answers TEST PAPERS)
NR 503 • Tue Jun 03 2025

Explore the full breakdown of the NR 503 Midterm and Final Exams. Download the Latest NR 503 EXAMS.
About the NR 503 MIDTERM & FINAL Exams:
Basically, you will complete two major exams in NR 503:
- Midterm Exam
- Final Exam
Both of which are designed to evaluate your understanding of the population health model, epidemiological analysis, and application of evidence-based interventions.
🔗 Access the WHOLE EXAMS BUNDLE Resource:
👉 [Click to Download Bundle for NR 503 Midterm and Final Exams 2025/2026 Latest Update PDF Download]
Instant PDFs | A+ Graded | 50% Discount | Up-to-Date | 100% PASS Rate Support
NR 503 Midterm Exam Breakdown:
The Midterm typically covers Weeks 1–4 and includes:
|
Topic |
Key Areas |
|
Epidemiological Triad |
Agent, Host, Environment |
|
Types of Epidemiologic Studies |
Descriptive, Analytical, Experimental |
|
Measures of Risk |
Incidence, Prevalence, Odds Ratio, Relative Risk |
|
Disease Surveillance Systems |
Local, State, National (CDC, WHO) |
|
Outbreak Investigation |
Steps, Patterns, Index Cases |
|
Screening Principles |
Sensitivity, Specificity, Predictive Value |
|
Health Promotion Theories |
Health Belief Model, Pender’s Health Promotion Model |
|
Levels of Prevention |
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary |
The Question Types are:
- Multiple choice
- True/False
- Case scenario analysis
Tip: Know how to apply epidemiologic models to real-world community health situations.
NR 503 Final Exam Breakdown:
The Final Exam is cumulative, but primarily emphasizes Weeks 5–8, including:
|
Topic |
Key Areas |
|
Social Determinants of Health |
Education, Income, Environment |
|
Health Disparities |
Race, Access, Cultural Barriers |
|
Public Health Ethics |
Principles of Autonomy, Justice, Nonmaleficence |
|
Health Policy and Advocacy |
Policy cycles, Stakeholders, Advocacy Roles |
|
Global Health Trends |
Infectious disease control, International partnerships |
|
Disaster Preparedness |
Public health response systems, Phases of disaster |
|
Environmental Health |
Toxins, Exposure Risk, Air/Water Quality |
Also expect questions on:
- Interpreting graphs and epidemiological data
- Designing population-level interventions
- Analyzing case studies on outbreaks or public health crises
Need Study Help or Test Banks?
We have complete, well-organized study guides, verified test banks, and actual NR 503 Midterm and Final Exam versions from previous semesters to help you pass with confidence.
Get PDF Downloads with Real Questions + Answers
Including:
NR 503 MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 2025/2026 Q&A PDF Download Graded A+
NR503 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Latest Update 2025/2026 Q&A PDF Download
NR 503 EPIDEMIOLOGY FINAL EXAM Q&A Latest Update 2025/2026 PDF Download
NR 503 MIDTERM EXAM LATEST UPDATE 2025/2026 Q&A PDF Download
Here is a FREE Sample for NR 503 FINAL EXAM Study Guide:
Week 5 (Chapter 2)
1. Populations at Risk for Chronic Health Conditions & the Role of the Advanced Practice Nurse (APN):
-
Common Risk Factors:
Unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco use. -
Childhood Risk:
Conditions before birth and early childhood affect adult health. For instance, low birth weight is linked with higher rates of hypertension, heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. -
Risk Accumulation with Age:
Aging increases the impact of modifiable risk factors over time. -
Underlying Determinants of Chronic Diseases:
Globalization, urbanization, population aging, and policy environments drive social, economic, and cultural change. -
Poverty and Chronic Disease:
Poverty is both a cause and consequence of chronic illness. Poor populations face higher risks and have less access to healthcare services. Psychosocial stress is a contributing factor.
Levels of Preventative Health Actions:
Primary Prevention
-
Aims to prevent disease or injury before it occurs.
-
Done by:
-
Preventing exposure to hazards
-
Modifying risky behaviors
-
Increasing resistance to illness/injury
-
-
Nurse Role: Educators promoting healthy behaviors.
-
Examples:
-
Legislation against hazardous products (e.g., banning asbestos)
-
Promoting seatbelt and helmet use
-
Educating on healthy eating, exercise, not smoking
-
Immunization programs
-
Secondary Prevention
-
Aims to reduce the impact of a disease/injury that has already occurred.
-
Done by:
-
Early detection and treatment
-
Preventing recurrence
-
Rehabilitation to restore health
-
-
Nurse Role: Early detection, risk management, lifestyle modification.
-
Examples:
-
Screenings (e.g., mammograms for breast cancer)
-
Aspirin use and diet/exercise post-heart attack
-
Modified work duties for recovering individuals
-
Tertiary Prevention
-
Aims to soften the impact of ongoing illness or injury.
-
Done by:
-
Managing long-term, complex conditions
-
Improving functionality and life quality
-
-
Nurse Role: Implementing and adapting care plans, behavior changes.
-
Examples:
-
Stroke or cardiac rehab
-
Chronic disease management (e.g., diabetes, arthritis)
-
Support groups and vocational rehab
-
Health Disparities and Vulnerable Populations:
-
Minorities are often at the lower end of the socioeconomic spectrum. Other at-risk groups include the homeless, immigrant workers, and refugees.
-
APNs must differentiate between cultural and socioeconomic causes of behavior.
-
Helpful Resource: Cross-Cultural Health Care Program (CCHCP) – provides materials and training to improve cultural competence.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health:
-
APRNs can collaborate with sectors like housing, education, and community groups to gather data and monitor inequalities.
-
Examples of Social Determinants:
-
Poverty
-
Educational level
-
Racism
-
Income
-
Poor housing
-
-
Consequences of Inequality:
-
Poor life quality
-
Lower self-rated health
-
Multiple chronic conditions
-
Limited resources
-
Premature death
-
Data-Driven Public Health Practice:
-
Assessment: APRNs must use accurate data to evaluate interventions and monitor community/population health indicators.
-
Partnerships:
Work with community members to:-
Identify health priorities
-
Build social capital
-
Use outcome data to advocate for policy change
-
Resources to Reduce Health Disparities:
-
National Partnership for Action (NPA):
Aims to eliminate health disparities by uniting private/public stakeholders around priority health topics (e.g., patient safety, palliative care, care coordination). -
Quality Alliance Steering Committee:
Health leaders working to improve healthcare quality and reduce costs. -
Strategies for APRNs:
-
Advocate for better insurance for underserved populations
-
Improve healthcare access in rural/urban poor areas
-
Study social environment, genetics, and population health
-
Promote minority participation in research
-
Use culturally appropriate communication and materials
-
Encourage community partnerships
-
Support minority recruitment into healthcare careers
-
Latest Uploads
- ISYE 6414 Final Correctly Answered 2025 Update
- ISYE 6414 Final Actual Test 2025 Updated Graded A+
- ISYE 6414 Midterm Summer 2025/2026 Exam Questions ...
- ISYE6414 2025 Summer Midterm TEST Questions and 10...
- ISYE6414 2025/2026 Summer Midterm COMPLETE PREP Ex...
- ISYE 6414 Final EXAM Questions and 100% Correct An...
- NAVEDTRA 15009B, CH 6 EXAM Questions and Answers L...
- NAVEDTRA 15009B, Ch 2 Exam Questions and Verified ...
- NAVEDTRA 15009B Chapter 1 Exam Questions and Answe...
- NAVEDTRA 15009B Chapter 3 Exam Correctly Answered ...
- NAVEDTRA 15009B Chapter 4 EXAM Questions and Answe...
- NAVEDTRA 15009B Chapter 6 Exam Questions and Answe...
- NAVEDTRA 15009B, YEOMAN (YN), CHAPTER 5, TRAVEL EX...
- NRTC NAVEDTRA 14233A ASN 4 EXAM Correctly Answered
- NRTC NAVEDTRA 14300A ASN 1 Questions and Answers
- NRTC NAVEDTRA 14300A ASN 3 EXAM Correctly Answered...
- YN NRTC Navedtra 15009B Ch 3-4 Questions and Answe...
- Yeoman chapter 3 Exam Questions and Correct Answer...
- Nicet Level 1 Study Guide Questions and Verified A...
- NICET Level 1 inspection and Testing Exam Question...
- STR practice test Questions and Answers
- STR Practice Exam 2 Questions and Verified Answers
- STR (CRQ terms, strategies) Correctly Answered Lat...
- STR Exam Questions and Verified Answers Latest Upd...
- IAAI CFI and NFPA 921 Exam Questions and Answers L...
- 2025 WSC Full Set–Pocketpwaa Exam Questions and Co...
- World Scholars Cup Questions and Answers 2025/2026...
- World Scholars Cup Questions and Verified Answers
- 2025 WSC MASTER SET Questions and Answers Latest
- Child Growth and Development CGDR DCF Correctly An...
- RNRF DCF Test Questions and Answers
- RNRF DCF Study Guide Correctly Answered Latest Upd...
- RNRF DCF Exam Questions and Answers
- FL DCF 40 Hrs, CHILD CARE FACILITIES RULE AND REGU...
- DCF-Child Growth and Development (CGDR) Correctly ...
- CGDR DCF Exam Questions and Answers
- ATCN review Questions and Correct Answers
- ATCN Pretest Exam Questions and Answers Latest
- ATCN review Questions and Answers Latest Update
- ATCN 2025 Chapter 3 Shock Exam Correctly Answered ...
- CFT monitor certification Exam Correctly Answered
- CA DMV AMBULANCE TEST Questions and Answers Latest
- Triple AAA Drivers Education Section Quiz Answers ...
- AAA Drivers Final Exam Questions and Answers Updat...
- AAA Exam Questions Chapter 4 Correctly Answered
- AAA Test Questions Chapter 7 Q&A Latest Update
- AAA Drivers Ed Midterm Correctly Answered
- AAA Drivers ED FINAL EXAM Questions and Answers La...
- NC Notary Public study guide Questions and Answers...
- NC Notary Public Study Guide Correctly Answered
- Tennessee Timeshare License Exam Questions and Ans...
- Tennessee National Portion REAL ESTATE EXAM Correc...
- Final Exam TN Real Estate Course Questions and Ans...
- Tennessee (state exam) Real Estate Questions and A...
- TN Real Estate State Test Questions and Answers 20...
- real estate TN EXAM Questions and Answers
- Real Estate Tennessee State Exam Questions and Ans...
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Improvement, Total Qu...
- Healthcare Quality Improvement and Risk Management...
- HCQM-Patient Safety Exam Questions and Answers
- HCQM Final Exam Questions and Answers
- LMR Georgettes 2025 Qbank PMHNP Certification Exam...
- FTCE PROFESSIONAL(Actual) EXAM Questions and Answe...
- ATI Mental Health Proctored Exam Review Questions ...
- ATI fundamentals practice test B Questions and Ans...
- FUNDAMENTALS EXAM #1 ATI Questions and Answers 202...
- Ati nutrition proctored Exam Correctly Answered 20...
- ATI Nutrition Proctored Exam Questions and Answers...
- ATI Nutrition Proctored Exam study Questions and A...
- GA Pest Employee Registration Exam Questions and A...
- Utah Basic Esthetics State Board Exam Questions an...
- Utah Basic Esthetics State Board Exam Questions an...
- VITA Certification Exam Questions and Answers 2025...
- VITA Session 1 Quiz Questions and Answers 2025-202...
- VITA Intake, Interview Review Test Q&A Latest 2025...
- VITA Basic Test Questions and Answers 2025-2026
- VITA Certification Test Questions and Answers 2025...
- Liberty University NBST 515 New Testament Orientat...
- GC201 Proficiency, Building Rooms and Beds CH 4 Q&...
- Grand Central TEST Q&A Latest Update
Popular Uploads
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
 Grand Central TEST Q&A Latest Update 12 pages
Grand Central TEST Q&A Latest Update 12 pages -

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
 NUR 205 exam 2 Q&A Latest Update 58 pages
NUR 205 exam 2 Q&A Latest Update 58 pages -

-
 NUR 205 Final Exam Q&A Latest Update 89 pages
NUR 205 Final Exam Q&A Latest Update 89 pages -

-
 NUR 205 Exam 3 Q&A Latest Update 22 pages
NUR 205 Exam 3 Q&A Latest Update 22 pages -

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-
 Nims 800 Exam Q&A Latest Update 6 pages
Nims 800 Exam Q&A Latest Update 6 pages -

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-





